

学习资源
科普文章
构型Format的重要性:几何结构定义了双特异性抗体的功能(二) [1]
双/多特异性抗体的构型format对于抗体的各个功能参数有重要影响,本文是关于综述Dickopf, S.et al, Format and geometries matter: Structure-based design defines the functionality of bispecific antibodies. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020. 18: p. 1221-1227摘译的第二部分,上期微信第一部分讨论了抗体format对于不同作用机制的影响,包括:1)受体激活;2) 受体阻断,抑制其与配体的结合,配体可能是可溶性的或者在效应细胞 (E)膜表达上的;3) 受体内化;4) 受体集聚;5) 受体结合;6) 效应细胞 (E) 的重定向,与目标细胞的结合,具体可参考:构型Format的重要性:几何结构定义了双特异性抗体的功能(一)
利用ADCC的抑瘤机制
引发针对肿瘤的细胞毒性效应是多抗的一个重要作用机制[2]。模拟ADCC(抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性)效应是其中的策略之一。该概念基于用抗体靶向癌细胞以及随后通过其 Fc 受体结合 NK 细胞。NK 细胞的激活反过来导致靶细胞杀伤[3]。双抗可以通过其Fc 区与NK 细胞表面上的Fc 受体(FcγRIII,CD16)结合,或者通过其不同的抗原结合域分别与肿瘤特异性抗原和 CD16结合。在这两种情况下,双抗的组成和format都会影响 ADCC 诱导功效。
依赖于Fc区的ADCC诱导效应
基于Fc 介导NK 细胞募集的双抗设计面临的挑战是需要确保 Fc区与 CD16 的空间可及性。例如,N 端或 C 端融合的 scFv有不同的ADCC诱导能力,范围从完全能力到 ADCC 活性丧失(图1、图2和图3)[4]。这些效应很可能是由添加的结合区和/或结合的靶抗原对 FcγRIII 与 NK 细胞相互作用的空间位阻引起的,其不仅取决于双抗format,还取决于靶抗原表位(epitope)的选择,因此需要分别单独进行实验评估。
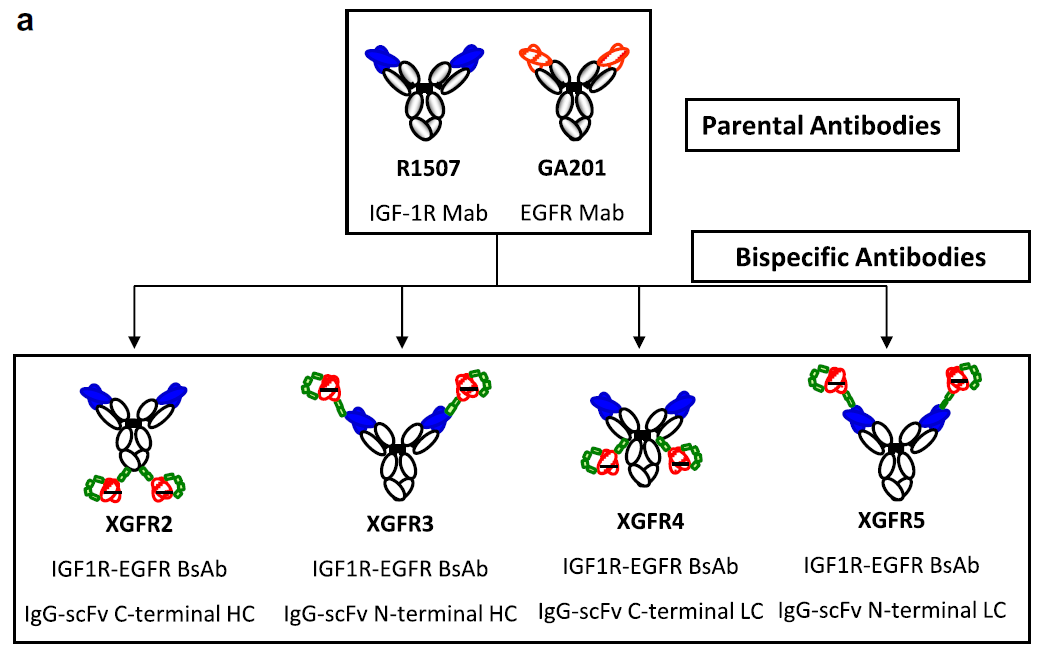
Fig. 1. Design of EGFR/IGF-1R (XGFR) molecule set. (a) Schematic diagram of the generation of VH44-VL100 disulfide stabilized (black bar) bispecific antibodies from the parental antibody molecules. The XGFR bispecific molecules contain N- and C-terminal scFvs fusions based on the antibody GA201 = EGFR (red striped), at the heavy and light chain of the antibody R1507 = IGF-1R (royal blue).
图 1. EGFR/IGF-1R (XGFR) 分子组的设计。(a) 从亲代抗体分子生成 VH44-VL100 二硫化物稳定(黑条)双特异性抗体的示意图。XGFR 双特异性分子在抗体 R1507 = IGF-1R(宝蓝色)的重链和轻链处包含基于抗体 GA201 = EGFR(红色条纹)的 N 端和 C 端 scFvs 融合。
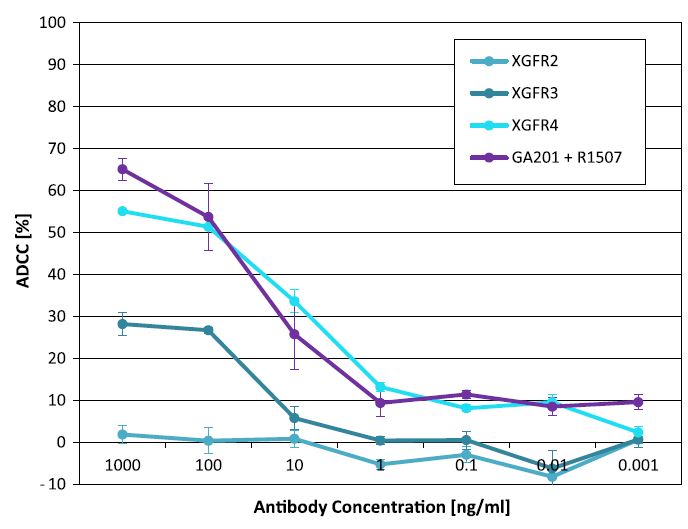
Fig. 2. xCELLingence ADCC induction of H322M cells after 5 h incubation with NK92 cells. The tumor cells and effector cells at a ratio of 1:3 were incubated for 5 h with 1000, 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 and 0.001 ng/ml of the XGFR and R1507 + GA201 antibodies. The antibody dilutions were performed at an equal molar ratio.
图 2. H322M 细胞与 NK92 细胞孵育 5 小时后的 xCELLingence ADCC 诱导。将比例为 1:3 的肿瘤细胞和效应细胞与 1000、100、10、1、0.1、0.01 和 0.001 ng/ml 的 XGFR 和 R1507 + GA201 抗体孵育 5 小时。以等摩尔比进行抗体稀释。
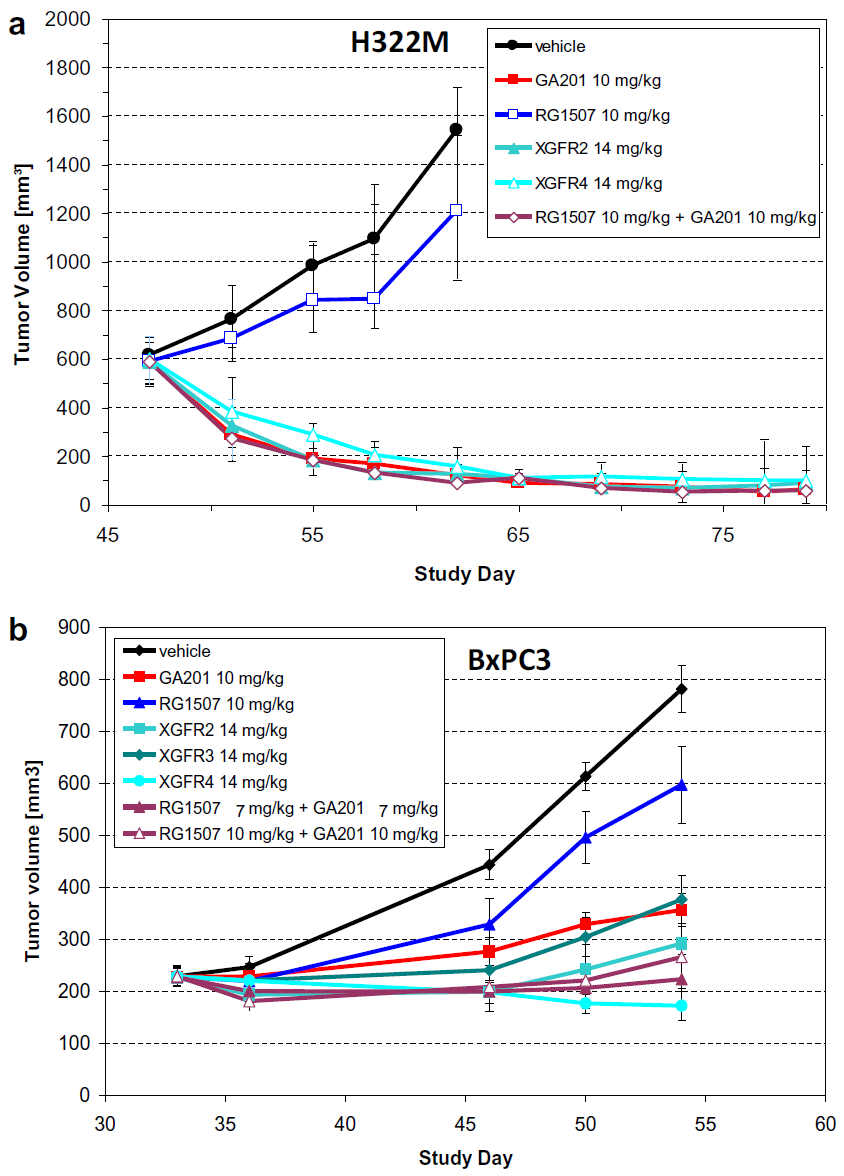
Fig. 3. Inhibition of tumor growth in human BxPC3 pancreatic and H322M lung subcutaneous xenograph model. Female SCID beige mice were injected subcutaneously with (a) H322M (2X 107/mouse) and in (b) BxPC3 (2X106/mouse) tumor cells. When a tumor volume of between 200 and 250 mm3 had been reached the mice were randomized, according to tumor volume, and divided 10–14 animals per group. The groups were treated once weekly with GA201 (10 mg/kg) and R1507 (10 mg/kg) the monotherapies, XGFR 2, 3 and 4 (14 mg/kg), the combination of GA201 (10 mg/kg) + R1507 (10 mg/kg) and saline solution (vehicle). The route of administration was by intravenous injection. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly and the means of the ±SD of 10 animals are shown.
图 3. 人 BxPC3 胰腺和 H322M 肺皮下异种移植模型中肿瘤生长的抑制。雌性 SCID 米色小鼠皮下注射 (a) H322M(2X 107/小鼠)和 (b) BxPC3(2X106/小鼠)肿瘤细胞。当肿瘤体积达到 200 至 250 mm3 时,根据肿瘤体积将小鼠随机分配,每组 10-14 只动物。这些组每周接受一次 GA201 (10 mg/kg) 和 R1507 (10 mg/kg) 单一疗法,XGFR 2、3 和 4 (14 mg/kg),GA201 (10 mg/kg) + R1507 的组合 (10 毫克/千克)和盐水溶液(车辆)。给药途径为静脉注射。肿瘤体积每周测量两次,并显示 10 只动物的±SD 平均值。
不依赖于Fc区的ADCC诱导效应
不依赖于Fc区,而是通过抗原结合域结合CD16的双抗,其诱导ADCC的功效同样取决于结合剂和format的选择。例如,Reusch 等人表明,结合肿瘤相关抗原 (TAA) CD30 和 CD16A 的双抗在ADCC诱导方面,具有二价 CD16A 结合的 TandAb优于单价结合的Diabody (图4和图5)[5]。
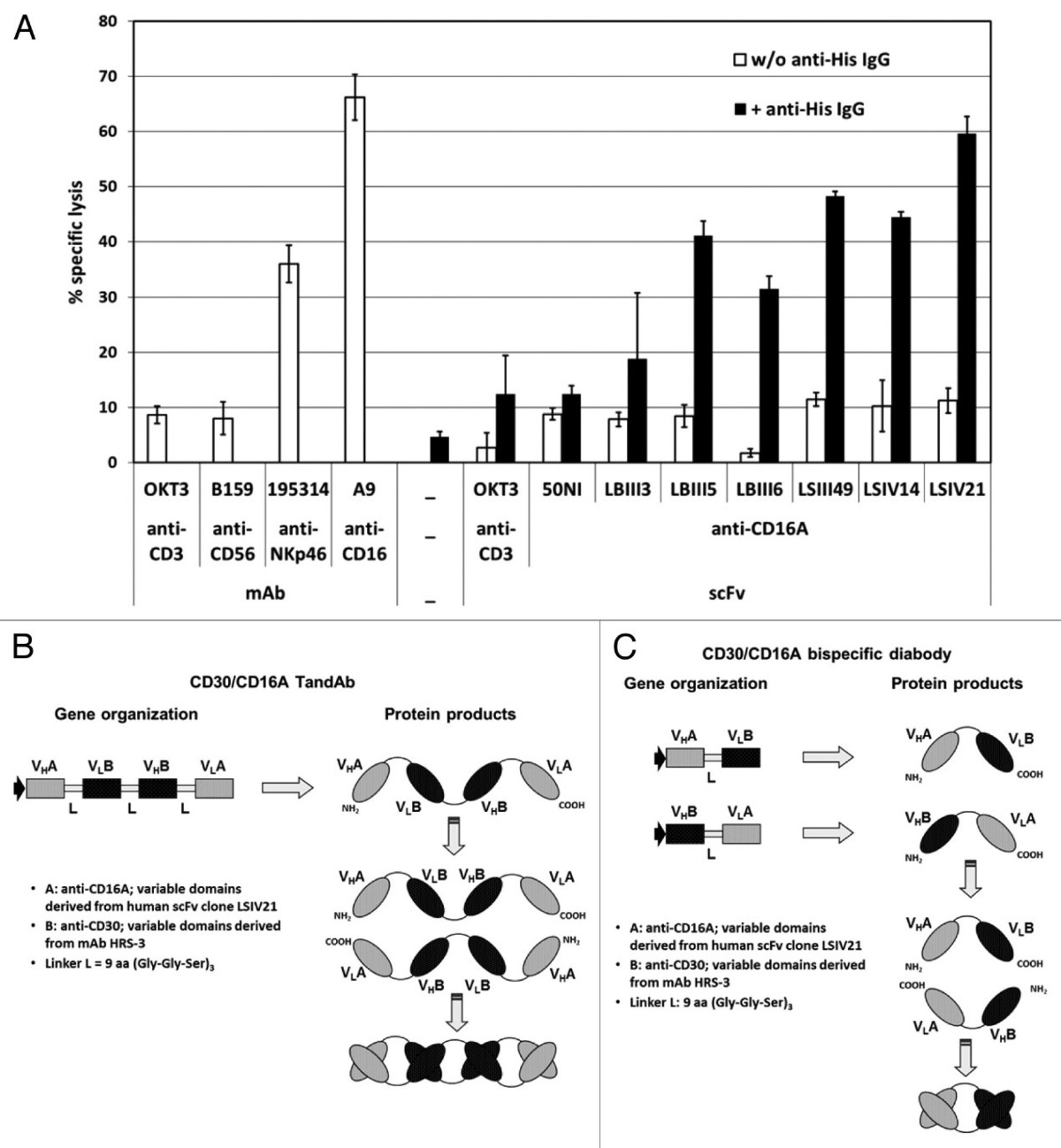
Figure 4. Selection of anti-CD16A-specific scFv for activation of NK cells and construction of bispecific CD30/CD16A TandAb and diabody. (A) Induction of redirected cell lysis with affinity matured anti-CD16A scFvs. 1 × 104 calcein-labeled FcγRII+ murine mastocytoma P-815 target cells were incubated in triplicate with freshly isolated and enriched human NK cells at an effector-to-target ratio of 10:1 in the presence of 1 µg/mL of the indicated scFv or IgGs with or without the addition of 1 µg/mL anti-His IgG1, clone 13/45/31–2, for 3 h. Percentage of specific target cell lysis was calculated from the measured fluorescence counts in the culture supernatant. Mean values and standard deviations from triplicates are plotted. (B and C) Schematic representation of the gene organization and domain order of the bispecific CD30/CD16A TandAb (B) and diabody (C). VHA and VLA represent the variable anti-CD16A domains that are derived from the human scFv clone LSIV21 isolated from Affimed's phage display library. VHB and VLB stand for the murine anti-CD30 Fv domains that are derived from the HRS-3 IgG. The HRS-3 hybridoma-derived light chain contains two mutations in framework 1: tyrosine at L23, instead of the conserved cysteine that forms a disulfide bond with CysL88, and asparagine at L20, which is a potential glycosylation site. The residues at L20 and L23 were restored to the original amino acids in the germline sequence. The linker peptides (L) are of 9 amino acids length and consist of three Gly-Gly-Ser repeats.
图 4. 用于激活 NK 细胞和构建双特异性 CD30/CD16A TandAb 和双抗体的抗 CD16A 特异性 scFv 的选择。(A) 用亲和力成熟的抗 CD16A scFvs 诱导重定向细胞裂解。1 × 104 钙黄绿素标记的 FcγRII+ 鼠肥大细胞瘤 P-815 靶细胞与新鲜分离和富集的人 NK 细胞一式三份孵育,效应物与靶标的比例为 10:1,存在 1 µg/mL 指定的 scFv 或添加或不添加 1 µg/mL 抗 His IgG1 的 IgG,克隆 13/45/31–2,持续 3 小时。从培养上清液中测量的荧光计数计算特定靶细胞裂解的百分比。绘制一式三份的平均值和标准偏差。(B 和 C) 双特异性 CD30/CD16A TandAb (B) 和双抗体 (C) 的基因组织和结构域顺序的示意图。VHA 和 VLA 代表可变的抗 CD16A 结构域,这些结构域源自从 Affimed 的噬菌体展示库中分离的人类 scFv 克隆 LSIV21。VHB 和 VLB 代表源自 HRS-3 IgG 的鼠抗 CD30 Fv 结构域。HRS-3 杂交瘤来源的轻链在框架 1 中包含两个突变:L23 处的酪氨酸,而不是与 CysL88 形成二硫键的保守半胱氨酸,以及 L20 处的天冬酰胺,这是一个潜在的糖基化位点。L20 和 L23 处的残基恢复为种系序列中的原始氨基酸。接头肽 (L) 的长度为 9 个氨基酸,由三个 Gly-Gly-Ser 重复序列组成。
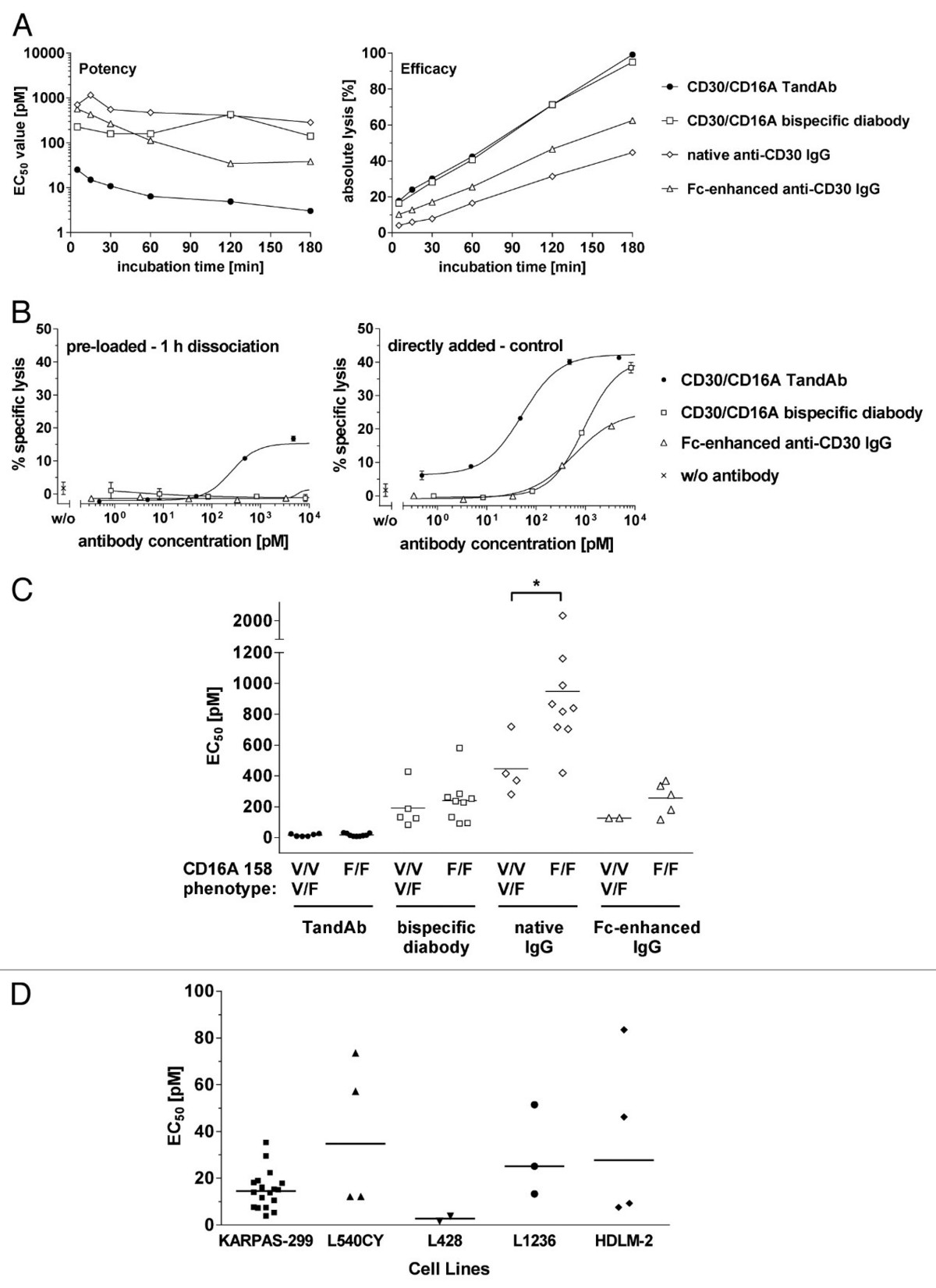
Figure 5. Comparison of CD30/CD16A TandAb and diabody, anti-CD30 IgG and Fc-enhanced anti-CD30 IgG in cytotoxicity assays. (A) Kinetics of antibody-mediated target cell lysis. 1 × 104 calcein-labeled KARPAS-299 target cells were incubated for the indicated time periods with increasing concentrations of CD30/CD16A TandAb, CD30/CD16A diabody, anti-CD30 IgG and Fc-enhanced anti-CD30 IgG together with freshly isolated human NK cells at an E:T ratio of 5:1. Percent specific target cell lysis was calculated from the fluorescent calcein released into the cell culture supernatant from apoptotic target cells. EC50 values (potency) and maximal target cell lysis (efficacy) were determined by nonlinear regression for all antibodies and plotted. (B) Residual cytotoxicity of pre-opsonized effector cells to measure antibodies’ retentions. Freshly isolated human NK cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of CD30/CD16A TandAb, diabody and Fc-enhanced anti-CD30 IgG for 15 min at 37 °C, washed twice and then incubated for 1 h at 37 °C to allow dissociation of the bound antibodies. After an additional washing step, NK cells were used as effector cells in a 3 h cytotoxicity assay with calcein-labeled KARPAS-299 target cells at an E:T ratio of 4.4:1 (pre-loaded – 1 h dissociation). As a control, NK cells were pre-incubated in the absence of antibodies before they were used as effector cells together with added antibodies in the same cytotoxicity assay (directly added - control). Mean values and SD from duplicates of one out of two independent experiments are shown. (C) Potency of TandAb, diabody and IgG in relation to the CD16A 158 polymorphism. The EC50 values for TandAb, diabody and anti-CD30 IgG were determined in several independent 3 h cytotoxicity assays on KARPAS-299 target cells with NK cells as effector cells isolated from unrelated donors as described and plotted in the diagram together with the mean values shown as bars. The CD16A 158 phenotype of the NK cells was assessed by flow cytometry after staining of the NK cells with the CD16 158V-specific mAb MEM-154. NK cells were rated as CD16A 158F/F when the fluorescence signal was at background level. The asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05). (D) Cytotoxic potency of the TandAb against a panel of five CD30+ cell lines. The EC50 values of the TandAb were determined in independent 3 h cytotoxicity assays on target CD30+ cells, with NK cells as effectors, isolated from independent donors, at a 1:5 ratio. Mean values for each cell line are shown as horizontal bars.
图 5. CD30/CD16A TandAb 和双抗体、抗 CD30 IgG 和 Fc 增强的抗 CD30 IgG 在细胞毒性测定中的比较。(A) 抗体介导的靶细胞裂解动力学。将 1 × 104 钙黄绿素标记的 KARPAS-299 靶细胞与浓度递增的 CD30/CD16A TandAb、CD30/CD16A 双抗体、抗 CD30 IgG 和 Fc 增强的抗 CD30 IgG 以及新鲜分离的人 NK 一起孵育指定的时间段 E:T 比例为 5:1 的细胞。从凋亡靶细胞释放到细胞培养物上清液中的荧光钙黄绿素计算特异性靶细胞裂解百分比。EC50 值(效力)和最大靶细胞裂解(功效)通过非线性回归确定所有抗体并作图。(B) 预调理效应细胞的残留细胞毒性,用于测量抗体的保留。将新鲜分离的人 NK 细胞与浓度递增的 CD30/CD16A TandAb、双抗体和 Fc 增强的抗 CD30 IgG 在 37°C 下孵育 15 分钟,洗涤两次,然后在 37°C 下孵育 1 小时以允许解离 结合抗体。在额外的洗涤步骤后,NK 细胞被用作效应细胞,用于 3 小时的细胞毒性测定,使用钙黄绿素标记的 KARPAS-299 靶细胞,E:T 比例为 4.4:1(预加载 - 1 小时解离)。作为对照,NK 细胞在没有抗体的情况下预孵育,然后在相同的细胞毒性测定中将它们用作效应细胞以及添加的抗体(直接添加 - 对照)。显示了两个独立实验中的一个重复的平均值和 SD。(C) TandAb、双抗体和 IgG 与 CD16A 158 多态性相关的效力。TandAb、双抗体和抗 CD30 IgG 的 EC50 值是在 KARPAS-299 靶细胞上的几个独立的 3 小时细胞毒性测定中确定的,其中 NK 细胞作为效应细胞从不相关的供体中分离出来,如图所示,并与所示的平均值一起绘制作为bar。在用 CD16 158V 特异性 mAb MEM-154 染色 NK 细胞后,通过流式细胞术评估 NK 细胞的 CD16A 158 表型。当荧光信号处于背景水平时,NK 细胞被评为 CD16A 158F/F。星号 (*) 表示统计显著性 (P < 0.05)。(D) TandAb 针对一组五个 CD30+ 细胞系的细胞毒性效力。TandAb 的 EC50 值是在对目标 CD30+ 细胞进行的独立 3 小时细胞毒性测定中确定的,其中 NK 细胞作为效应子,从独立供体中分离出来,比例为 1:5。每个细胞系的平均值显示为水平条。
在下期微信会分享该综述中T 细胞结合衍生物 T cell-engaging derivatives的评述,敬请读者期待。
本文仅作信息分享,不代表礼进生物公司立场和观点,也不作治疗方案推荐和介绍。如有需求,请咨询和联系正规医疗机构。
参考文献:1.Dickopf, S., G.J. Georges, and U. Brinkmann, Format and geometries matter: Structure-based design defines the functionality of bispecific antibodies. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020. 18: p. 1221-1227.
2.Bluemel, C., et al., Epitope distance to the target cell membrane and antigen size determine the potency of T cell-mediated lysis by BiTE antibodies specific for a large melanoma surface antigen. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 2010. 59(8): p. 1197-1209.
3.Wang, W., et al., NK Cell-Mediated Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in Cancer Immunotherapy. Frontiers in Immunology, 2015. 6.
4.Croasdale, R., et al., Development of tetravalent IgG1 dual targeting IGF-1R–EGFR antibodies with potent tumor inhibition. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2012. 526(2): p. 206-218.
5.Reusch, U., et al., A novel tetravalent bispecific TandAb (CD30/CD16A) efficiently recruits NK cells for the lysis of CD30+ tumor cells. mAbs, 2014. 6(3): p. 727-738.





 沪公网安备 31011502015333号
沪公网安备 31011502015333号